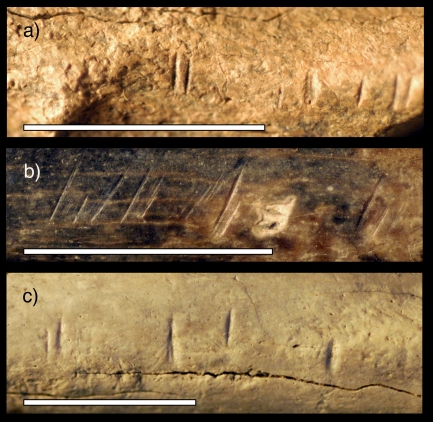
Close-up photos of three fossil animal specimens from the same area and time horizon as the fossil hominin tibia studied by the research team. These fossils show similar cut marks to those found on the hominin tibia studied. The photos show (a) an antelope mandible, (b) an antelope radius (lower front leg bone) and (c) a large mammal scapula (shoulder blade). (Image courtesy Brian Pobiner)
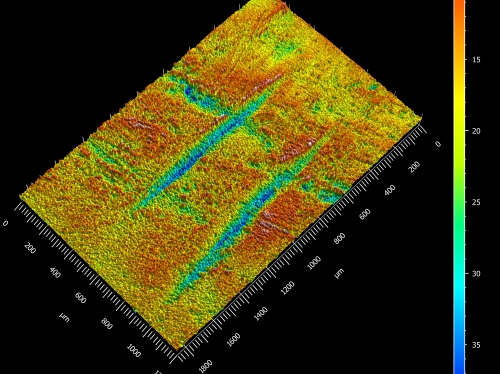
In a new study published today, June 26, in Scientific Reports, Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History paleoanthropologist Briana Pobiner and her co-authors describe nine cut marks on a 1.45 million-year-old left shin bone from a relative of Homo sapiens found in northern Kenya. Analysis of 3D models of the fossil’s surface revealed that the cut marks were dead ringers for the damage inflicted by stone tools. This is the oldest instance of this behavior known with a high degree of confidence and specificity.
By themselves, the cut marks do not prove that the human relative who inflicted them also made a meal out of the leg, but Pobiner said this seems to be the most likely scenario. She explained that the cut marks are located where a calf muscle would have attached to the bone—a good place to cut if the goal is to remove a chunk of flesh. The cut marks are also all oriented the same way, such that a hand wielding a stone tool could have made them all in succession without changing grip or adjusting the angle of attack.