
The Smithsonian at 175
The Smithsonian was founded August 1846. We mark this historic milestone and imagine the Institution’s next 175 years.
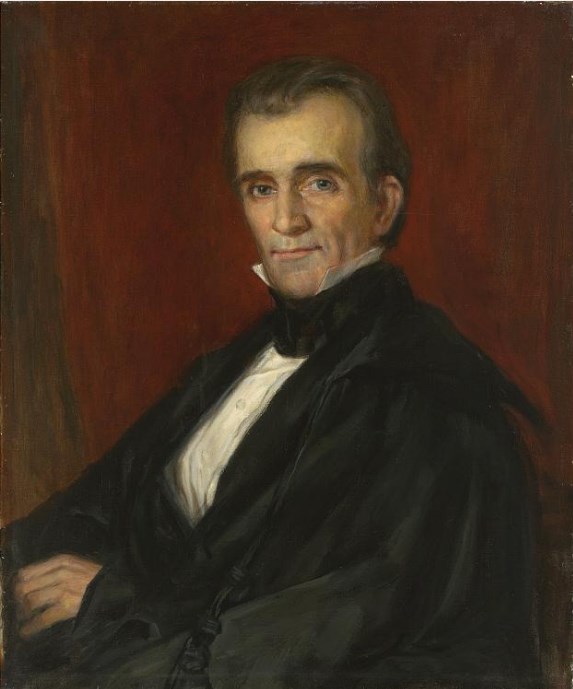
The Smithsonian Institution was established with funds from James Smithson (1765–1829), a British scientist who left his estate to the United States to found “at Washington, under the name of the Smithsonian Institution, an establishment for the increase and diffusion of knowledge.” On August 10, 1846, the U.S. Senate passed the act organizing the Smithsonian Institution, which was signed into law by President James K. Polk.
Congress authorized acceptance of the Smithson bequest on July 1, 1836, but it took another ten years of debate before the Smithsonian was founded. Once established, the Smithsonian became part of the process of developing an American national identity—an identity rooted in exploration, innovation, and a unique American style. That process continues today as the Smithsonian looks toward the future.
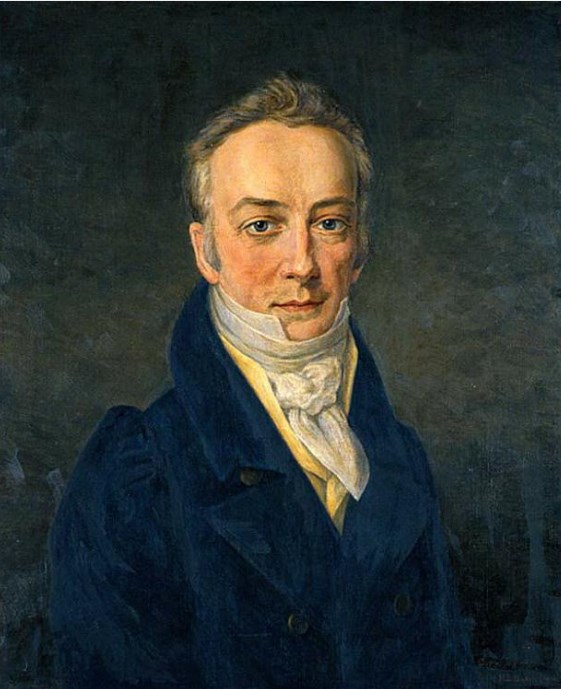
Smithson, the illegitimate child of a wealthy Englishman, had traveled much during his life, but had never once set foot on American soil. Why, then, would he decide to give the entirety of his sizable estate—which totaled half a million dollars, or 1/66 of the United States' entire federal budget at the time—to a country that was foreign to him?
Some speculate it was because he was denied his father's legacy. Others argue that he was inspired by the United States' experiment with democracy. Some attribute his philanthropy to ideals inspired by such organizations as the Royal Institution, which was dedicated to using scientific knowledge to improve human conditions. Smithson never wrote about or discussed his bequest with friends or colleagues, so we are left to speculate on the ideals and motivations of a gift that has had such significant impact on the arts, humanities, and sciences in the United States.
Visitors can pay homage to Smithson with a visit to his crypt, located on the first floor of the Smithsonian Castle.
Learn more about James Smithson »

Smithson died in 1829, and six years later, President Andrew Jackson announced the bequest to Congress. On July 1, 1836, Congress accepted the legacy bequeathed to the nation and pledged the faith of the United States to the charitable trust. In September 1838, Smithson's legacy, which amounted to more than 100,000 gold sovereigns, was delivered to the mint at Philadelphia. Recoined in U.S. currency, the gift amounted to more than $500,000.
After eight years of sometimes heated debate, an Act of Congress signed by President James K. Polk on Aug. 10, 1846, established the Smithsonian Institution as a trust to be administered by a Board of Regents and a Secretary of the Smithsonian. Since its founding, more than 175 years ago, the Smithsonian has become the world's largest museum, education, and research complex, with 21 museums, the National Zoo, and nine research facilities.
Learn more about our history from Smithsonian Institution Archives »